Microsoft used its AI-powered Safety Copilot to find 20 beforehand unknown vulnerabilities within the GRUB2, U-Boot, and Barebox open-source bootloaders.
GRUB2 (GRand Unified Bootloader) is the default boot loader for many Linux distributions, together with Ubuntu, whereas U-Boot and Barebox are generally utilized in embedded and IoT gadgets.
Microsoft found eleven vulnerabilities in GRUB2, together with integer and buffer overflows in filesystem parsers, command flaws, and a side-channel in cryptographic comparability.
Moreover, 9 buffer overflows in parsing SquashFS, EXT4, CramFS, JFFS2, and symlinks have been found in U-Boot and Barebox, which require bodily entry to take advantage of.
The newly found flaws impression gadgets counting on UEFI Safe Boot, and if the suitable situations are met, attackers can bypass safety protections to execute arbitrary code on the machine.
Whereas exploiting these flaws would probably want native entry to gadgets, earlier bootkit assaults like BlackLotus achieved this via malware infections.
“Whereas risk actors would probably require bodily machine entry to take advantage of the U-boot or Barebox vulnerabilities, within the case of GRUB2, the vulnerabilities might additional be exploited to bypass Safe Boot and set up stealthy bootkits or doubtlessly bypass different safety mechanisms, akin to BitLocker,” explains Microsoft.
“The implications of putting in such bootkits are vital, as this will grant risk actors full management over the machine, permitting them to regulate the boot course of and working system, compromise extra gadgets on the community, and pursue different malicious actions.”
“Moreover, it might end in persistent malware that is still intact even after an working system reinstallation or a tough drive substitute.”
Under is a abstract of the failings Microsoft uncovered in GRUB2:
- CVE-2024-56737 – Buffer overflow in HFS filesystem mounting because of unsafe strcpy on a non-null-terminated string
- CVE-2024-56738 – Facet-channel assault in cryptographic comparability perform (grub_crypto_memcmp not constant-time)
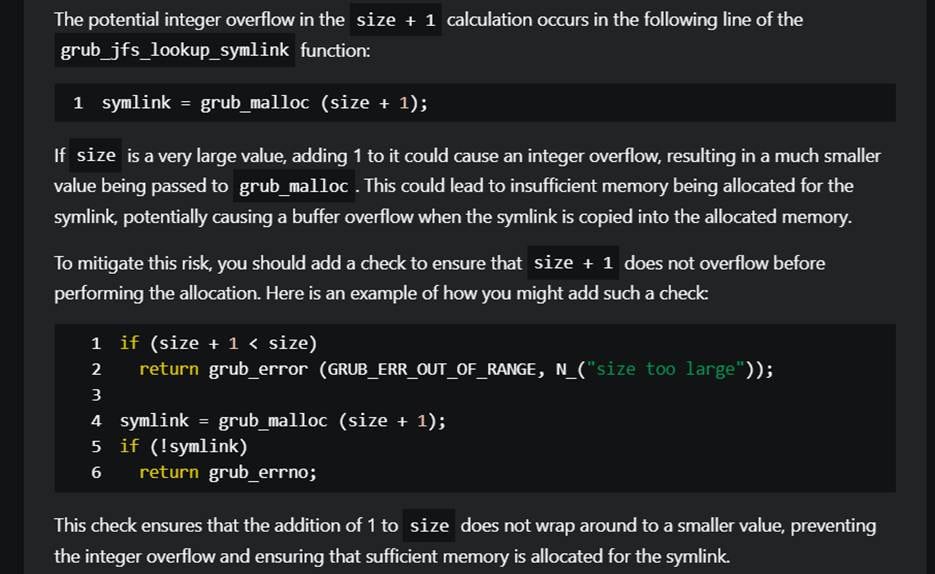
- CVE-2025-0677 – Integer overflow in UFS symbolic hyperlink dealing with results in buffer overflow
- CVE-2025-0678 – Integer overflow in Squash4 file studying results in buffer overflow
- CVE-2025-0684 – Integer overflow in ReiserFS symbolic hyperlink dealing with results in buffer overflow
- CVE-2025-0685 – Integer overflow in JFS symbolic hyperlink dealing with results in buffer overflow
- CVE-2025-0686 – Integer overflow in RomFS symbolic hyperlink dealing with results in buffer overflow
- CVE-2025-0689 – Out-of-bounds learn in UDF block processing
- CVE-2025-0690 – Signed integer overflow and out-of-bounds write in learn command (keyboard enter handler)
- CVE-2025-1118 – dump command permits arbitrary reminiscence learn (needs to be disabled in manufacturing)
- CVE-2025-1125 – Integer overflow in HFS compressed file open causes buffer overflow
The entire above flaws are rated medium severity, apart from CVE-2025-0678, which is rated “excessive” (CVSS v3.1 rating: 7.8).
Microsoft says Safety Copilot dramatically accelerated the vulnerability discovery course of in a big and sophisticated codebase, akin to GRUB2, saving roughly 1 week of time that will be required for handbook evaluation.
Supply: Microsoft
Not solely did the AI instrument determine the beforehand undiscovered flaws, however it additionally supplied focused mitigation suggestions that might present pointers and speed up the issuing of safety patches, particularly in open-source initiatives supported by volunteer contributors and small core groups.
Utilizing the findings within the evaluation, Microsoft says Safety Copilot discovered comparable bugs in initiatives using shared code with GRUB2, akin to U-boot and Barebox.
GRUB2, U-boot, and Barebox launched safety updates for the vulnerabilities in February 2025, so updating to the most recent variations ought to mitigate the failings.


